Authentication chain¶
Understanding the authentication chain helps explain how GeoServer authentication works. The authentication chain processes requests and applies certain authentication mechanisms. Examples of authentication mechanisms include:
- Username/password—Performs authentication by looking up user information in an external user database
- Browser cookie—Performs authentication by recognizing previously sent browser cookies (also known as “Remember Me”)
- LDAP—Performs authentication against an LDAP database
- Anonymous—Essentially performs no authentication and allows a request to proceed without any credentials
Multiple authentication mechanisms may be active within GeoServer at a given time. The following figure illustrates the flow of a generic request.
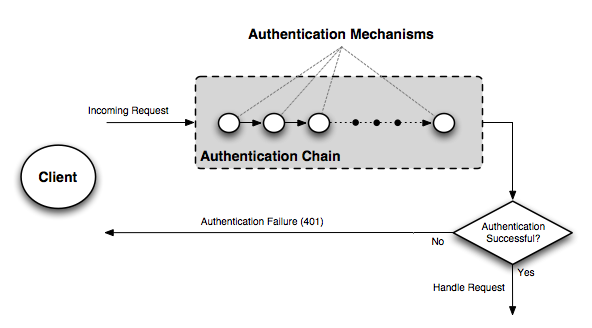
Flow of a request through the authentication system
Before dispatching a request to the appropriate service or handler, GeoServer first filters the request through the authentication chain. The request is passed to each mechanism in the chain in order, and each is given the chance to authenticate the request. If one of the mechanisms in the chain is able to successfully authenticate, the request moves to normal processing. Otherwise the request is not routed any further and an authorization error (usually a HTTP 401) is returned to the user.
Filter chain and provider chain¶
In the case of GeoServer, the authentication chain is actually made up of two chains: a filter chain, which determine if further authentication of a request is required, and a provider chain, which performs the actual authentication.
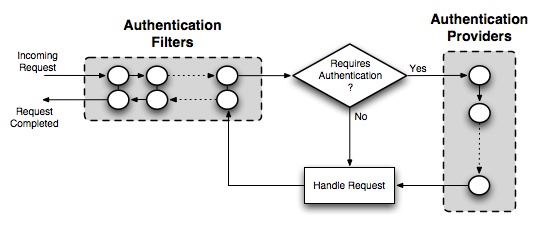
Detail of authentication chain, showing filter chain and provider chain
The filter chain performs a variety of tasks, including:
- Gathering user credentials from a request, for example from Basic and Digest Authentication headers
- Handling events such as ending the session (logging out), or setting the “Remember Me” browser cookie
- Performing session integration, detecting existing sessions and creating new sessions if necessary
- Invoking the authentication provider chain to perform actual authentication
The filter chain is actually processed twice, before and after the request is handled.
The provider chain is concerned solely with performing the underlying authentication of a request. It is invoked by the filter chain when a filter determines that authentication is required.